Ancient African tribes are immersed in culture, and each region of Africa has its own distinct traits. This lesson looks at the many different and wonderful communities that once existed in ancient Africa.
There were multiple ancient African “tribes” or civilizations. Africa is a vast continent with a diverse landscape that includes rainforests, savannas, and deserts.
Each location had its own own culture to go with it. We are continually learning about ancient Africa; much of what we know about African cultures comes from oral histories passed down through the generations.
Griots, or oral storytellers, have the unique role of remembering and transmitting their culture’s history, much like a historian. They have been telling their people’s stories for hundreds of years and continue to do so today, handing along history through stories and songs.
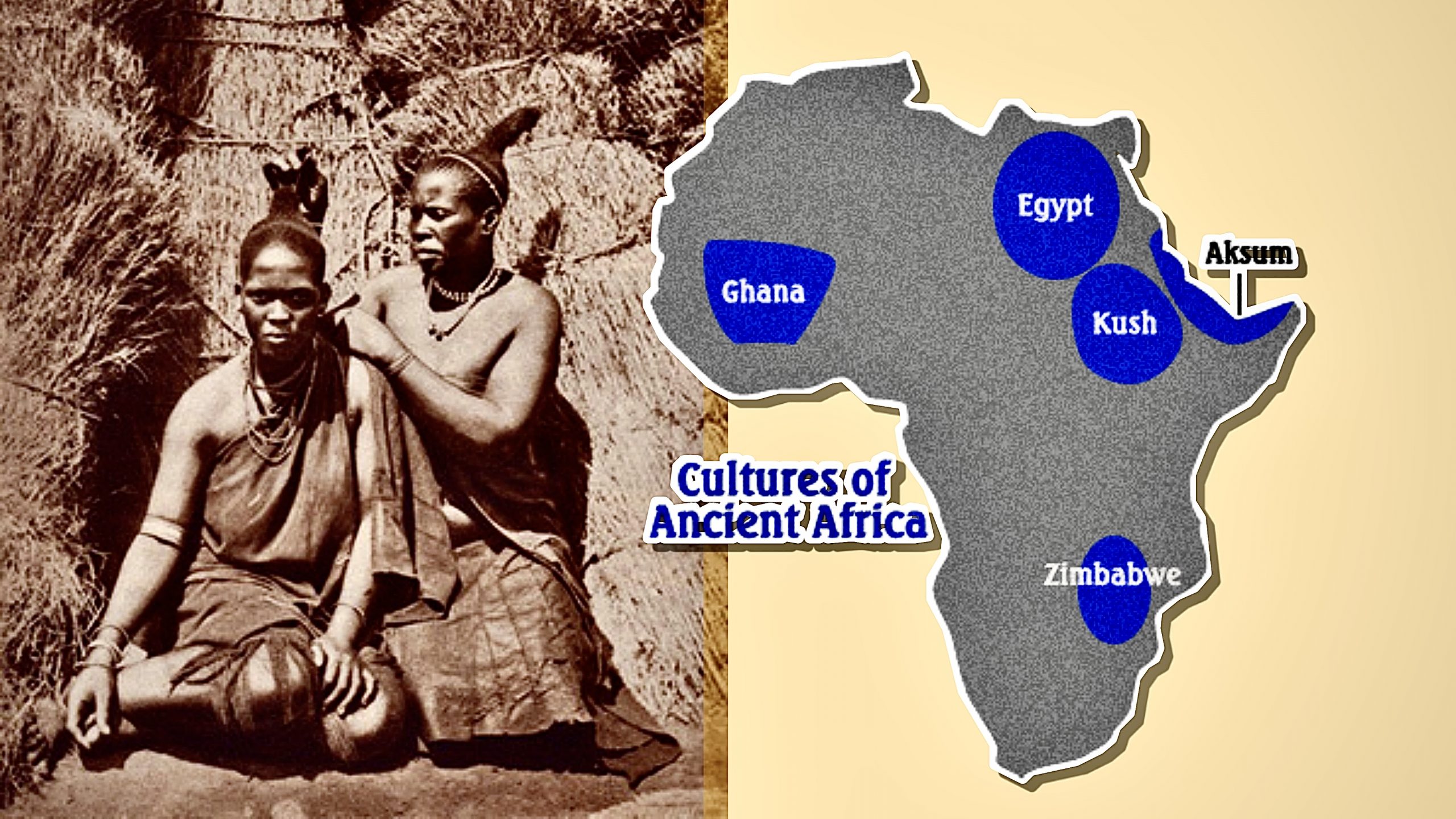
Some of the largest cultures and kingdoms from ancient Africa are:
- The Kingdom of Kush
Along the Nile River, the Kingdom of Kush was located immediately below Ancient Egypt. They lived from roughly 1070 B.C.E. to 300 C.E. The Kush people were known for their bows and arrows, which helped them gain an advantage in combat. The majority of inhabitants in the Kush region were cotton, wheat, and barley growers. The Kush society valued women and had a number of queen leaders.
- The Kingdom of Aksum
The Kingdom of Aksum existed from around 400 B.C.E. until 940 C.E., making it one of Africa’s longest civilizations. The Aksum people, who lived near the Red Sea coast, were important traders and merchants, and their city became an important trade port for African and Egyptian merchants, as well as traders from India and Persia. As a result of the numerous various civilizations that traveled through its ports, their culture was incredibly diversified.
- The Kingdom of Ghana
From around 300 to 1100 C.E., the Kingdom of Ghana was located in the western section of the continent, in the savanna grassland. Ghanaians were largely farmers, but they were recognized for their iron and gold, and metalsmiths were often regarded as strong magicians in their culture. These’magicians’ used fire to create powerful weapons from iron and gold, making them powerful warriors.
- The Kingdom of Zimbabwe
The Kingdom of Zimbabwe did not rise to prominence until around 1200 C.E., making it one of Africa’s later civilizations. The people of Zimbabwe lived in southern Africa, where they had a significant trading presence and remarkable architectural talents. They built towers and enormous stone walls that can still be visible today, despite the fact that they only lasted roughly 200 years.
- The Egyptian Kingdom
Ancient Egypt, located along the Nile River in Africa’s northeast, is by far the longest-lasting and most influential civilization. Ancient Egyptians were experts in science, math, and writing, and they even practiced medicine.
Ancient Egypt was ruled by the Assyrians, Persians, and Greeks (Alexander the Great) between 3150 and 30 B.C.E., but it had previously been ruled by the Assyrians, Persians, and Greeks (Alexander the Great) in the third and fourth centuries B.C.E. Ancient Egypt’s culture was advanced, with exquisite clothing, art, and intricate religious systems.
 The African History Truly African
The African History Truly African