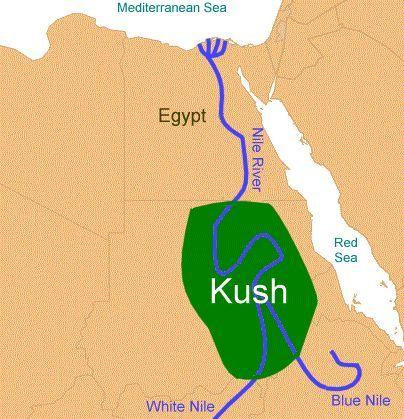
The Kush Empire was centered in North East Africa, in the south of Ancient Egypt. The central towns of Kush were located along the Nile River, along the White Nile River, and the Blue Nile River.
For more than 1400 years the Kingdom of Kush managed to remain a regional empire in Africa. In the 2nd millennium B.C., this ancient Nubian Kingdom hit its peak, when it controlled an extensive region of the River Nile in the present day Sudan.
Kingdom of Kush become powerful in northern Africa because it was a financial center running a valuable ivory, flame, iron, and gold marketplace in particular.
The Kingdom had been a trade partner and an Egyptian military opponent — Kush Empire also controlled Egypt as the twenty-fifth Dynasty — and adapted some of the traditions of Ancient Egypt.
Some of the Egyptian gods were worshiped by the Kushites; they mummified themselves and created their separate pyramids. Now there are over 200 pyramids in the region around the former Kushite capital of Meroe – more than those in the whole of Egypt.
The Period of Kush Empire
Kush Kingdom persisted for more than 1400 years. It was first set up around 1070 BCE after it got its independence from Egypt. It has sharply became the superpower Kingdom in North-East Africa. Kush took over Egypt in the 727 BCE and reigned before the Assyrians entered. After Rome defeated Egypt and gradually fallen in the 300s CE, the kingdom began to fall.
The Capitals of Kush Kingdom
Two varying capitals were in the Kingdom of Kush. Napata was the first base. In the northern Kush region, Napata was situated along the Nile River. During Kush’s control, Napata operated as the capital city. At around 590 BCE, Kushites moved to Meroe and made it their new capital. Meroe had stronger protection from the war with Egypt far south. It was also an iron-working center, a major advantage to the Kingdom.
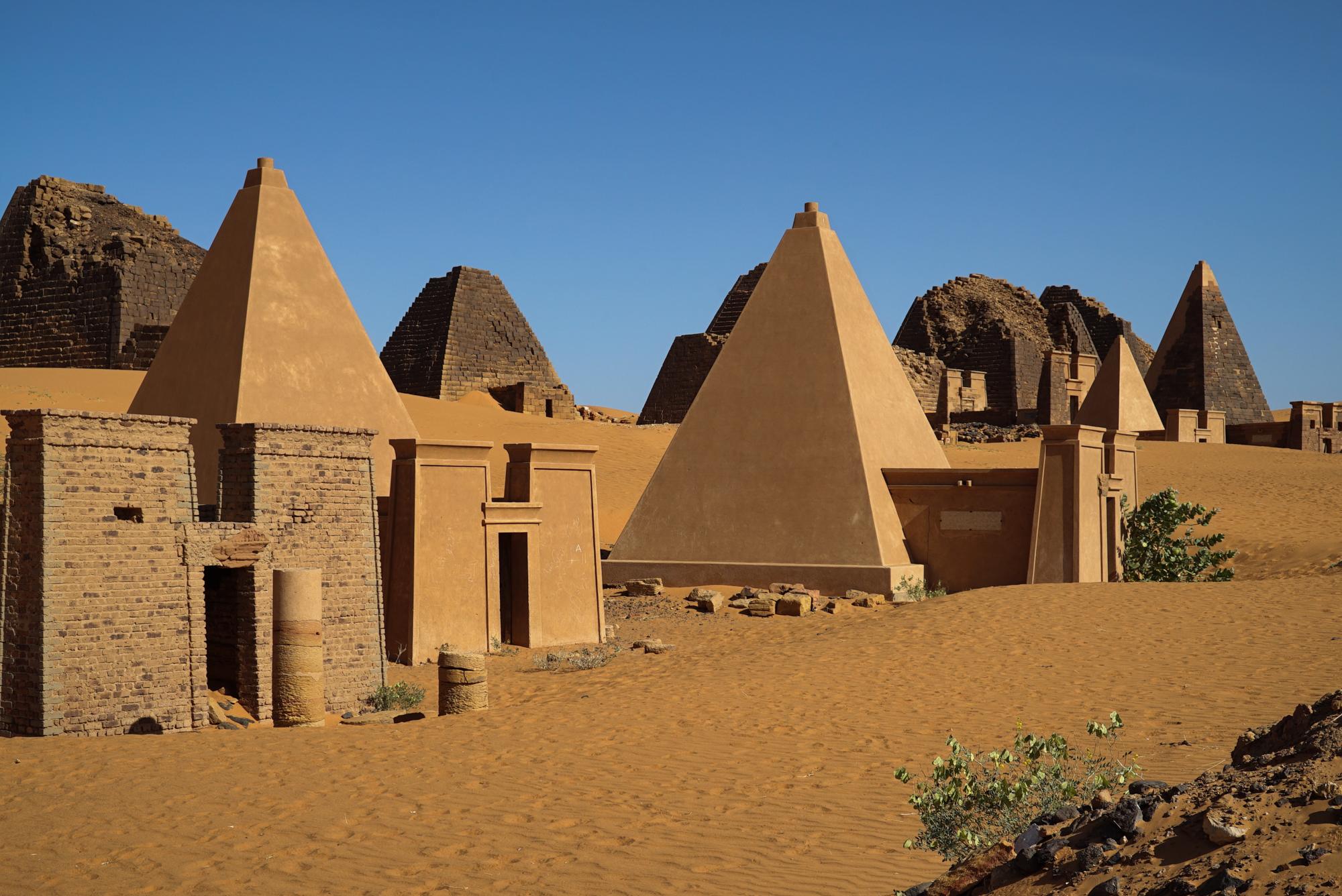

Kush and Egypt
In several ways, like governance, tradition, and belief, the Kush kingdom mirrored ancient Egypt. Like the Egyptians, at burial sites, the Kushites set up pyramids, adoring the Egyptian gods, and mummifying the dead. Kush’s ruling elite also saw itself as Egyptian in several aspects.
Resources of Ancient Kush
Gold and iron formed two of Ancient Kush’s most valuable resources. The gold enabled Kush get rich because the Ancient Egyptians and other neighboring states could exchange it. Iron was the earliest metal of its kind. The strongest tools and guns were made out of it.
Kushites Culture
Beyond the Pharaoh and the political elite, priests used to be the most powerful social class in the Kingdom of Kush. They passed laws and talked with the gods. Artisans and scribe were under the priests. Artisans worked on the gold and iron which were the most important of the Kushite Empire. Farmers also were praised for providing the state with food. The lower surface is servants, workers, and slaves.
The same as the Egyptians, throughout the lives of the Kushites religion played a major role. They respected the life after death very much. Women were much respected and could also be leaders in the kingdom of Kush. There were several queens in the Kushite Kingdom.
Interesting truths about the Kush kingdom
- In the fight, Kushites were known for their archers, and the bow and arrow were often portrayed in the crafts of the Ancient Kushites. The region was also referred as the “Land of the Bow” for its popular archers.
- Piye, who captured Egypt and then became pharaoh of Egypt, was among Kush’s most prominent kings.
- Farmers were the majority in the Kingdom of Kush. They had wheat and barley as the main crops. Cotton was also used for making clothes.
- Kushites pyramids were smaller than those of Egypt. Burial chambers were placed under the pyramids, many of those pyramids were built around the capital of Meroe and they still exist up to date.
- The priests were very powerful that they could make up their minds about when the king would die.
- Kushites did not live for long, people were expected to live for only 20 to 25 years old.
- Apart from iron and gold which were the primary resources, Kushites were also involved in ivory, slavery, feathers, wild animal hides, and incense.
 The African History Truly African
The African History Truly African

